DRILLING MACHINE WORKING AND TYPES

A drilling machine drills holes in components or workpieces using drill bits, also known as multi-point cutting tools. These tools significantly impact the Material Removal Rate (MRR)—unlike single-point tools (such as those used in a lathe), which remove material slowly, multi-point tools remove it much faster, increasing productivity.
The drilling machine plays a crucial role in workshops. It creates cylindrical holes of specific diameter and depth in metal workpieces. While various machines can produce holes, the drilling machine specializes in drilling and related operations.
This machine allows quick and cost-effective drilling. The process involves rotating a drill bit, which cuts into the material to form a cylindrical hole. First, a center punch makes an indentation at the target location. Then, the operator presses the rotating drill onto the mark and feeds it into the material until reaching the desired depth.
Drilling Machine Operations
Although drilling is the main function, this machine also performs several other hole-related operations using different tools. Common operations include:
Reaming – Enlarges or finishes a hole to precise dimensions.
Boring – Enlarges an existing hole with better accuracy.
Counterboring – Creates a flat-bottomed enlargement at the top of a hole.
Countersinking – Produces a conical surface at the hole entrance.
Tapping – Cuts internal threads into a drilled hole.
Larger and heavy-duty drilling machines are usually mount directly on the floor. A vertical column sits on the base and supports both the table and the power transmission components. You can move the table up and down along the column. The drill spindle, electric motor, and spindle speed control mechanism are all mounted on top of the column. Power transfers from the motor to the spindle via a flat belt or a V-belt.
Main Parts of a Drilling Machine:
1. Base (Bed):
Manufacturers cast the base from cast iron because of its high compressive strength, excellent wear resistance, and vibration absorption. The base supports the entire drilling machine structure.
2. Column:
The column is fixed vertically at the center of the base. It supports the swivel table and holds the power transmission system.
3. Swivel Table:
The swivel table attaches to the column and holds the machine vice, which grips the workpiece during drilling. You can raise or lower the table using rotational motion, and a locking nut secures it at the desired height.
4. Power Transmission System:
This system includes the motor, stepped pulleys, V-belt, and the spindle. It transmits motion from the motor to the spindle, allowing the drill bit to rotate at various speeds.
5. Hand Wheel:
Turning the hand wheel moves the spindle vertically, feeding the drill bit into the workpiece. A rack and pinion mechanism converts the hand wheel’s rotational motion into vertical linear movement.
6. Chuck:
The chuck holds the drill bit firmly in place.
Types of Drilling Machines:
Drilling machines come in various types and sizes depending on the application. Factors like type of operation, feed rate, cutting depth, spindle speed, spindle movement method, and accuracy requirements determine the specific model used.
The different types of drilling machines are:1. Portable drilling machine (or) Hand drilling machine 2. Sensitive drilling machine (or) Bench drilling machine 3. Upright drilling machine 4. Radial drilling machine 5. Gang drilling machine 6. Multiple spindle drilling machine 7. Deep hole drilling machine1.Portable drilling machineA portable drilling machine can be easily carrY and used anywhere in the workshop. These machines are commonly found in almost every workshop due to their compact and lightweight design. Their portability makes them ideal for on-site and overhead work, especially in automobile assembly and repair.
This type of machine uses a universal motor, allowing high-speed operation. It typically accommodates drill bits ranging from 12 mm to 18 mm in diameter and is best suite for drilling small-sized holes.
To operate it, the user holds the machine in one hand and secures the workpiece in a vice or clamp. This setup ensures stability and precision during drilling.
2. Sensitive Drilling Machine
This types of drilling machine used to drill small holes at high speeds in lighter jobs or work pieces. The machine may be mount on the bench or floor & the drilling work is started with the drill fed into the work piece by purely hand control.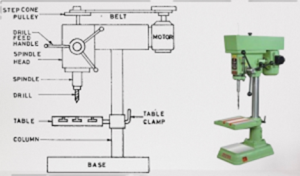
Sensitive Drilling Machine
Hand-feed allows the operator to directly sense the progress of the drill into the workpiece. If the drill begins to wear out or jams, the operator can immediately stop or adjust the feed to prevent the drill bit from breaking.
Because the operator constantly senses the cutting action, this type of machine is known as a sensitive drilling machine. It is capable of drilling small holes ranging from 0.35 mm to 15 mm in diameter and operates at high speeds, up to 2000 rpm.

Upright Drilling Machine
Operators use upright drilling machines to drill medium and large-sized holes. Based on the column type, these machines fall into two categories: round column and box column.
Radial Drilling Machine
A radial drilling machine is design for drilling medium to large and heavy workpieces. It features a heavy round column mounted on a large base, which supports a radial arm. The radial arm can be raise or lowered to accommodate workpieces of varying heights.
The drill head, mounted on the radial arm, can slide along the arm and rotate around the column, allowing flexible positioning. This unique movement is what gives the radial drilling machine its name.
base, column, radial arm, drill head and driving mechanism.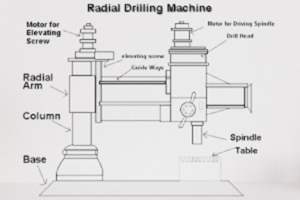 Construction of Radial Drilling Machine:The setup essentially consists of
Construction of Radial Drilling Machine:The setup essentially consists of- Base
- Column
- Radial Arm
- Motor for elevating the arm
- Elevating screw
- Guide ways
- Motor for driving drill spindle
- Drill head
- Drill spindle
- Table
- Base: It is made up of Cast Iron which possesses high compressive strength and good wear resistance. The base is used to support the assembly of parts on it and also absorbs the vibrations induced by the machine parts.
- Column: It is exactly placed at one end of a bed which can act as a support for rotating the radial arm in 360 degrees.
- Radial Arm: It is the arm which is connected to Column. The Drill head is slided from one end to another end by the guide ways.
- Motor: It is placed on the drill head for driving the work unit(Spindle of the Drill bit)
- Table: The machine vice is connected to a swivel table which can hold the workpiece for further operation.
- Flywheel or Hand wheel: It is connected to the spindle arrangement which is used to move up and down w.r.t. the work piece.
- Drive Head: It generally consists of two levers which by varying can increase or decrease the speed of chuck.
- Chuck: One end of the chuck is connected to the spindle arrangement and another end is connected to the drill bit(tool).
- Tool-Drill bit: The drill bit is used to drill the holes on the specimens.
- Work piece: It has to be fixed in the machine vice provided on the table.
 Tools used in a drilling machine
Different tools are used for performing different types of operations. The most commonly used
tools in a drilling machine are
1. Drill
2. Reamer
3. Counter bore
4. Countersink
5. Tap
1. Drill
A drill is a tool used to originate a hole in a solid material. A helical groove known as ‘flute’ is cut
along the length of the drill.
Different types of drills are
1. Flat Drill
2. Straight fluted drill
3. Twist drill
4. Center drillTwist drills are the type generally used in shop work. They are made of High speed steel (HSS) or High carbon steel. There are two types of twist drills namely (i) Straight shank twist drill and (ii) Taper shank twist drill. The diameter of the straight shank drill ranges from 2 to 16 mm. Taper shanks is provided on drills of larger diameter.Reamer
The tool used for enlarging and finishing a previously drilled hole is known as a reamer. It is a multi tooth cutter and removes smaller amount of material. It gives a better finish and accurate dimension.Counter bore
A Counter bore is a multi tooth cutting tool used for enlarging the top of the previously machined hole. It has three or four cutting teeth. The flutes on them may be straight or helical. Straight fluted tools are used for machining softer materials like brass and aluminium and for short depth of cut. Helical fluted counter bores are used for longer holesCountersink
A countersink has cutting edges on its conical surfaces. It has a similar construction of a counter bore except for the angle of the cutting edges. The angle of countersinks will generally be 60°, 82° or 90°. It is used for enlarging the top of the holes conically.
Tools used in a drilling machine
Different tools are used for performing different types of operations. The most commonly used
tools in a drilling machine are
1. Drill
2. Reamer
3. Counter bore
4. Countersink
5. Tap
1. Drill
A drill is a tool used to originate a hole in a solid material. A helical groove known as ‘flute’ is cut
along the length of the drill.
Different types of drills are
1. Flat Drill
2. Straight fluted drill
3. Twist drill
4. Center drillTwist drills are the type generally used in shop work. They are made of High speed steel (HSS) or High carbon steel. There are two types of twist drills namely (i) Straight shank twist drill and (ii) Taper shank twist drill. The diameter of the straight shank drill ranges from 2 to 16 mm. Taper shanks is provided on drills of larger diameter.Reamer
The tool used for enlarging and finishing a previously drilled hole is known as a reamer. It is a multi tooth cutter and removes smaller amount of material. It gives a better finish and accurate dimension.Counter bore
A Counter bore is a multi tooth cutting tool used for enlarging the top of the previously machined hole. It has three or four cutting teeth. The flutes on them may be straight or helical. Straight fluted tools are used for machining softer materials like brass and aluminium and for short depth of cut. Helical fluted counter bores are used for longer holesCountersink
A countersink has cutting edges on its conical surfaces. It has a similar construction of a counter bore except for the angle of the cutting edges. The angle of countersinks will generally be 60°, 82° or 90°. It is used for enlarging the top of the holes conically.Tap
A tap resembles a bolt and features three to four flutes cut across its threads. These flutes form the cutting edges and allow the tap to cut internal threads inside a drilled hole. Since the lower part of the tap is slightly tapered, it digs into the hole walls gradually. The square-shaped shank allows users to grip it securely using a tap wrench. It functions as a multi-point cutting tool.
Applications of Drill Machines
The primary function of a drill machine is to create holes of various sizes in solid materials. Depending on the specific task, different types of drills serve various applications:
Drill rigs drill water and oil wells.
Hand drills assist in screwing and fastening.
Electric pistol-grip drills are commonly used by builders, electricians, and plumbers for general masonry work.
Hammer drills are ideal for carpenters when drilling and fixing wooden parts.
Cordless drills prove useful in locations where electricity is not accessible.
Pillar drill machines (also known as drill presses) are used in commercial applications that require bulk production of drilled components in materials such as metal sheets, plastics, wood, glass, and construction materials.
The drill press allows users to easily control the drilling speed and capacity by adjusting the power supply. The machine’s performance capacity varies depending on factors like:
Pillar diameter
Spindle nose
Spindle travel
Spindle speed
Type of electric motor used
Industries such as automotive, printing, and engineering widely use drill presses to improve strength, precision, and productivity. In sectors that require mixing and grinding of solids and liquids, milling-cum-drilling machines are often used.
Maintenance Tips
Lubricate regularly
Apply the correct lubricant frequently to minimize friction. This reduces wear on moving parts and extends the machine’s lifespan.Inspect for wear and tear
Look for signs of damage caused by vibration, shock, heat, or friction. Replacing worn components early prevents major breakdowns.Keep the machine clean
Check all seals and filters regularly. Clean or replace them as needed. Clean breathers to avoid vacuum formation, which may draw contaminants into the system. Clean all holes and surfaces on the machine after use.Sharpen cutting components
Keep drill bits, end mills, precision cutters, and lathe tools sharp to maintain cutting accuracy and efficiency. Dull tools reduce output quality and increase material waste.
Check alignment specifications– Drilling machines often have multiple components. Losing alignment can greatly affect the quality of work. You can check alignment by performing a test job and subsequently measuring the resulting parts. If the specifications are inaccurate, you will need to realign the machine.
Good records of maintenance and repair schedules– Some parts such as fluids, electrical systems and tracks have to be checked frequently for preventive measures. Keeping proper records allows you to have the tools and spare parts necessary on hand to avoid extended downtime.
Maintenance records are also important for your employees’ safety. Preventive maintenance schedules diminish the machine downtime significantly.
Safety Precautions:- Always wear an eye protection when using your drill.
- Make sure that cutting tools are running smoothly before starting the operation
- Never place tools or even equipment on the drill table
- Keep your guard while operating
- Adjusting the machine while using it can be dangerous, make sure to adjust it while the machine is not running.
- Use a brush to clean away the chips



