Basic Fundamental Term of Electric power and energy

Basic Fundamental Term
“This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the basic fundamentals of electrical engineering, covering core concepts such as Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws, AC/DC circuits, electrical components, and safe wiring practices essential for beginners.”
Alternating current
Alternating current is a type of electric current that regularly changes direction and magnitude. Unlike direct current (DC), which flows in one direction, AC oscillates, making it essential for various electrical applications.

An ammeter
An ammeter is a device used to measure electric current in amperes. It is calibrated to accurately measure a wide range of current values. Typically, a shunt placed in parallel with the meter helps manage high current flows.
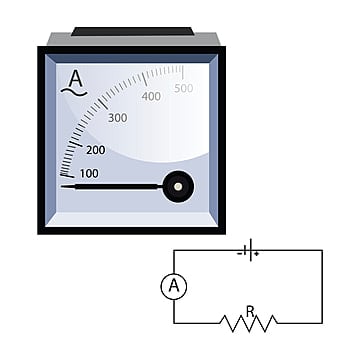
Circuit
A circuit is the path that an electric current follows. In a basic electrical circuit, three main components are present: a voltage source, a conductive path, and a resistor. However, circuits can consist of multiple components, such as generators, batteries, and various equipment, connected by wires or transmission lines.
Conduit
A conduitis a protective tube through which electrical wires or cables are routed to pass through different structural or architectural elements. It shields the wires from damage and ensures proper distribution throughout the system.
Wires
Wires are long, thin conductive metal pieces used for binding objects or transmitting electricity. They provide a pathway for electrical currents to flow efficiently. Common conductive materials for wires include copper and aluminum.
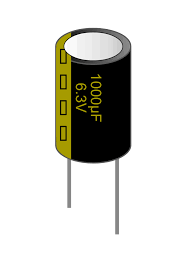
Capacitors
Capacitors are devices designed to store electrical charges. The ability of a capacitor to hold a charge is measured in farads, indicating the ratio of electric charge to voltage across the object.
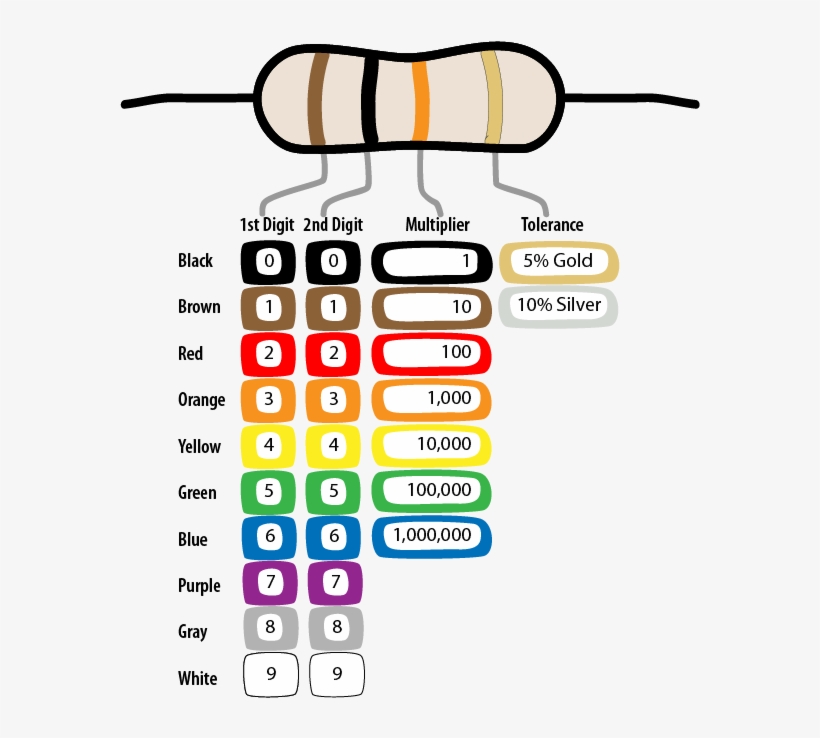
Resistors
Resistors are components that impede the flow of electric current. They regulate current flow, adjust signal levels, and perform various other functions in electronic circuits.
Conductors
Conductors are materials that allow electrical current to flow freely. Metals, such as copper and aluminum, are common examples of conductive substances due to their low resistance.

Insulators
Insulators are materials that prevent electrical current from flowing. They have tightly bonded electrons, inhibiting the movement of electric charge.

Current
Current refers to the flow of electric charge through a conductor, typically measured in amperes. It is often likened to the flow of water in a pipe.
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is a safety device that automatically interrupts electrical current flow in a circuit to prevent damage from overloads or faults.
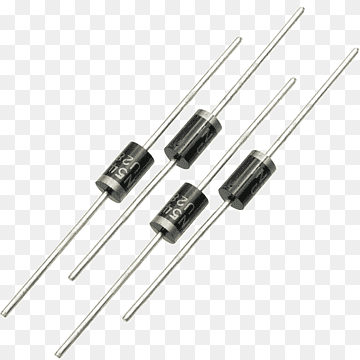
Diodes
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are commonly used in rectifier circuits and signal processing.
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in a solution. It plays a crucial role in battery operation, facilitating the movement of ions.
Impedance
Impedance refers to the resistance a circuit presents to the flow of alternating current. Unlike resistance, impedance considers both magnitude and phase in AC circuits.
Inductance
Inductance is a property of electrical conductors or circuits that induces an electromotive force when the current changes. It is measured in henries and affects the behavior of AC circuits.
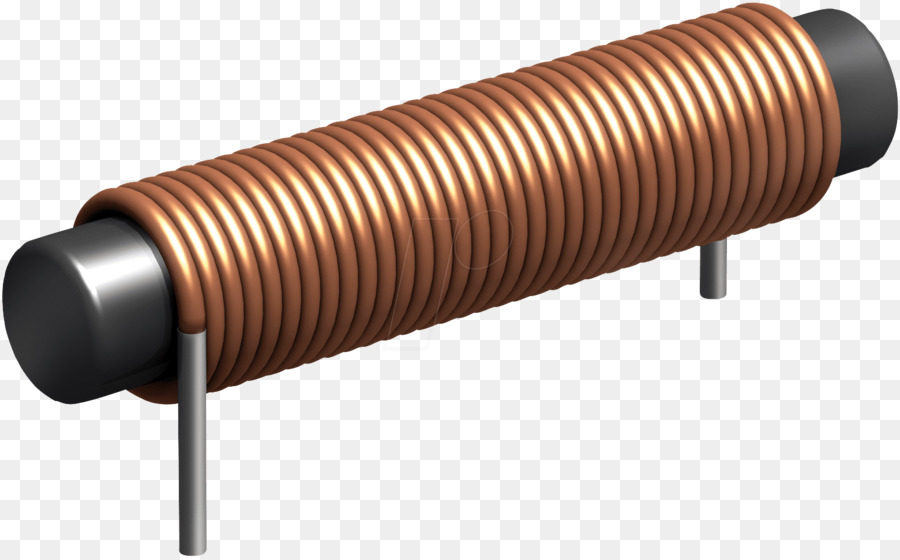
Inductor
An inductor is a coil of wire wound around a core material. It stores energy in the form of a magnetic field and is used in various electronic applications.
Ohmmeter
An ohmmeter is a device used to measure the electrical resistance of a circuit in ohms.

Power
Power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred in a circuit, measured in watts. It can be calculated using the formula P = IV, where P represents power, I represents current, and V represents voltage.
Reactive power
Reactive power is the portion of electrical power that sustains the electric and magnetic fields of AC equipment. It arises when current and voltage are out of phase and is measured in volt-amperes reactive (VAR).
Semiconductors
Semiconductors are materials with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. They are fundamental to modern electronics and include devices like transistors and diodes.
Short circuit
A short circuit occurs when current bypasses part of an electrical circuit, potentially causing damage or overheating.
Voltage
Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit, measured in volts. It drives the flow of electric charge (current) through a conductor.
Transistors
Transistors are semiconductor devices that amplify or switch electronic signals and power. They are vital components in electronic circuits.
Series circuit
In a series circuit, components are arranged sequentially, and the same current flows through each component.
Parallel circuit
In a parallel circuit, components are connected across common points, allowing multiple paths for current flow.
Polarity
Polarityrefers to the positive and negative ends of an electrical component or circuit, indicating the direction of current flow.
Ohms
Ohms are the unit of measurement for electrical resistance.
Ohm’s law
Ohm’s law states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, provided the temperature remains constant.
Farad
The farad is the unit of capacitance, measuring a capacitor’s ability to store charge.
Henry
The henry is the unit of inductance, measuring the ability of an inductor to induce voltage.
Generator
A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Fuse
A fuse is a safety device that interrupts excessive current flow in a circuit to prevent damage.
Frequency
Frequency is the number of cycles per second in an alternating current, measured in hertz (Hz).
Ferroresonance
Ferroresonance is a nonlinear resonance phenomenon that can occur in electrical circuits, potentially causing overvoltage and posing risks to equipment.
Electron
An electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle.
Electromotive Force
EMFis the voltage that drives current flow in a circuit.
Dielectric constant
The dielectric constant measures a substance’s ability to store electrical energy in an electric field.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a chemical process that decomposes substances using direct current.
Node
A node is a junction point between two or more branches in a circuit.
Loop
A loop is a closed path within an electrical circuit.
Mesh
A mesh is a closed path in a circuit that contains no other closed paths.
Branch
A branch is a single leg of a circuit containing a specific component.
Phasor
A phasor is a representation of sinusoidal quantities, such as voltage and current, in electrical circuits.
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between circuits using electromagnetic induction.
Voltmeter
A voltmeter measures the voltage difference between two points in a circuit.



