Detail Study of screen printing and Dyes
types of dyes and their properties

- Intense color.
Solubility.
Substantivity.
Fastness.
Nitro dyes area unit polynitro derivatives of phenols containing a minimum of one radical ortho or para to the hydroxyl. it’s accustome dye wool. It include 2 or a lot of aromatic rings (benzene, naphthalene).
Natural dyes are merely dye substances extract from natural sources. though the most supply of dyes for early times, they need for the most part been replace by artificial dyes, that area unit sometimes a lot of reliable, cheaper and may be equippe a lot of pronto.
Direct dyes: These dye staffs area unit usually Na salt of acid. they need direct affinity to plastic fiber. sorts of dyes and their properties area unit water soluble and desires salt addition within the dye tub, ought to be apply at basic or neutral condition. This dye workers is poor fastness to clean however cheaper.
These area unit the dyes which might be apply on to the materials from associate solution. These area unit most helpful for materials which might type H bonds with the coloring of materials.
Direct dyes
primarily replaced basic dyes and gained wide popularity because they eliminated the need for a mordant or binder when dyeing cotton. Although their colors are not as vibrant as those produced by basic dyes, direct dyes offer better fastness to light and washing. Post-treatments—such as diazotization and development—can further enhance this fastness.
Manufacturers use direct dyes on cotton, linen, rayon, wool, silk, and nylon.. These dyes sometimes have chemical group linkage –N=N- and high mass. they’re water soluble due to acid teams.
Direct orange twenty six could be a typical substantive dye.

Fig: Direct orange twenty six
Synthetic dye:
Dyes derived from organic or compound area unit called artificial dyes. samples of this category of dyes area unit Direct, Acid, Basic, Reactive dye, Mordant, Metal advanced, Vat, Sulphure, Disperse dye etc. artificial dyes quickly replaced the standard natural dyes.

They value less, they offer a massive vary of recent colours, and that they impart higher properties to the artificial materials dyes area unit currently classify in keeping with however they’re utilize in the coloring method.
Basic dyes: These sorts of dyes and their properties area unit usually ammonia sulphonium or auxonium salt, known for bright shade, water soluble & application on cotton & different plastic fiber and leathers.

Basic dyes were the first synthetic dyes develope from coal-tar derivatives. While modern developments have largely replaced them in textile dyeing, they still play a role in discharge printing and in coloring leather, paper, wood, and straw. More recently, manufacturers have successfully used basic dyes with certain man-made fibers, particularly acrylics.
Originally, dyers used basic dyes on wool, silk, linen, and hemp without a mordant. With a mordant like tannin, they could also dye cotton and other cellulosic fabrics. Basic dyes produce bright, intense colors and offer excellent fastness on acrylic fibers. They also work on basic dyeable variants of nylon and polyester.
Basic Brown one is associate example of a ion dye that’s pronto protonated beneath the pH a pair of to five conditions of coloring.
Acid dyes: with chemicals acid dyes belong to varied subclasses like nitro.nitroso, monoazo. diazo. xanthane. azine, quinoline, anthraquinone etc. These sorts of dyes and their properties ar water soluble and have affinity to wool, silk and nylon fibers. they’re apply to the fibers through neutral or dyestuff tub.
Acid dyes ar soluble anionic dyes, containing one or a lot of sulphonic acid substituents or alternative acidic teams. associate example of the category is Acid Yellow thirty six.

Fig: Acid yello36
Most artificial food colours fall during this class. The colouring method is reversible and should be delineate as follows:

Mordant Dyes:
Mordant dyes are among the oldest natural dyes. They do not have a direct affinity for textiles, but dyers can apply them to cellulose or protein fibers after treating the fabric with metallic salts (mordants). These dyes form insoluble complexes with metallic oxides, which then fix the color onto the fiber.
Sulfur Dyes:
Sulfur dyes are complex organic compounds that contain sulfur. Although insoluble in water, they become soluble under reducing conditions. Dyers primarily use sulfur dyes on cotton to produce economical dark shades. These dyes provide good wet fastness but have poor light fastness.
Azoic dyes: These aren’t readymade dyes. Fibers ar first of all fertilised with a coupling element like B-nepthol and so combined with a diazotised base to provide insoluble dye staffs into the fiber. Their main use on cotton however can also be color silk & fur.
Azo dyes contain a minimum of one radical (-N=N-) connected to 1 or usually 2 aromatic rings. These dyes ar used primarily for bright red shades in colouring and printing since most alternative categories of quick dyes ar lacking in smart red dyes. Azoic dyes, referr to as Naphthols within the trade, are literally factory-made within the cloth by applying one half the dye.
the opposite [*fr1] is then place on and that they mix to create the finished color. Unless they’re fastidiously apply and well washed, they need poor fastness to rubbing or crocking.
The production of dark-blue red early dye from the subsequent 2 parts is associate example.

Vat dyes: These sorts of dyes and their properties are in no time color on cotton & insoluble in water. they’re reduce by robust reductant to provide leuco-vat & at this stage they’re soluble in water. once impregnation they’re once more change to their original insoluble kind.

The vat dyes ar insoluble complicated polycyclic molecules supported the compound structure (ketoforms).
Vat Dyes
The term “vat” originates from the traditional indigo dyeing process, where indigo had to be reduce in a vat (container) to make it soluble for dyeing. Once applied to the fabric, the dye would oxidize and return to its insoluble form, becoming colorfast and durable.
Vat dyes are derive from compounds such as indigo, anthraquinone, and carbazole. They are widely use on cotton, linen, rayon, wool, silk, and occasionally on nylon.
These dyes are also use in continuous piece dyeing, particularly in a method known as the pigment application process, which combines the stability of vat dyes with high production efficiency.
Vat dyes are value for their exceptional fastness to light, washing, and chemicals, making them ideal for industrial and durable textile applications.
The dyeings made during this means have high wash and lightweight fastness.
An example of a dye is Vat Blue four (Indanthrene)
Reactive Dyes</strong>
data-start=”168″ data-end=”601″>Reactive dyes form valency (covalent) bonds with cellulose fibers, such as cotton, resulting in excellent wash fastness. These dyes are also suitable for wool, silk, and nylon. The dyeing process typically begins in a neutral bath, while fixation occurs in an alkaline bath. Because the dye molecules chemically bond with the fiber itself, the color becomes permanent and durable, even after repeated washing.
data-start=”603″ data-end=”943″>Reactive dyes are ideal for bleaching and dyeing cotton, wool, or silk fabrics. The reactive group in the dye chemically reacts with the hydroxyl or amino group of the fiber, making the shade long-lasting and vibrant. Various types of reactive dyes are use across the textile industry for their superior performance and vibrant shades.
Disperse Dyes Disperse dyes are specifically design for synthetic fibers, such as polyester, nylon, acrylic, and cellulose acetate. These dyes are only slightly soluble in water. They are apply by grinding the dye into a fine powder along with dispersing agents to create a stable suspension. The dye bath then contains dispersed dye particles that slowly diffuse into the fiber.
Originally develope for cellulose acetate fibers, disperse dyes are now widely used in dyeing polyester and other synthetics. Dyeing methods include high-temperature dyeing or carrier dyeing techniques.
Examples of disperse dyes include:
Disperse Yellow 3
Disperse Red 4
Disperse Blue 27
These dyes provide bright, vivid colors and are essential in the dyeing of synthetic textiles.

Nitro dyes ar polynitro derivatives of phenols containing a minimum of one chemical group ortho or para to the chemical group. it’s accustom dye wool. It include \
These coloring of materials don’t dye the material directly however need a binding agent called mordant. The mordant acts as a binding agent between the fibre and therefore the dye. Some dyes mix with metal salts (mordanting) to make insoluble coloured complexes (lakes). These materials ar typically used for the coloring of cotton, wool or alternative macromolecule fiber. The metallic precipitate is create within the fiber manufacturing in no time colours extremely immune to each light-weight and laundry.Example:
 Fig: Mordant dye
Fig: Mordant dyeConstruction and working of Rotary screen printing
The rotary screen machine square measure supported constant principle of automatically.
There square measure 2 strategies of print paste.
1.by using rubber blade of various hardness
2.by using the magnetic roll system.
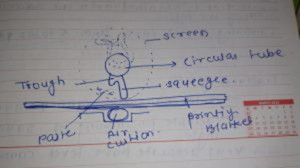
In initial technique, feeding the paste to the present blade and by Appling pressure pushing the paste through the screen to artefact,the use of rolls, plate or air cushion below every system.
In second technique, uses the magnetic roll system wherever the color is iron through a steel rod activat by a magnet below the printing table and looking on the scale of rod and quantity of pull applied by a magnet.
flat screen printing isn’t continuous however. Rotary-screen printing on the opposite hand is continuous. Rotating screens square measure used that square measure mechanically fed (by suggests that of pumps) with paste from within. Driving the screens are often done at either facet.
The value of continuous rotary-screen printing initial became apparent within the Sixties. The hollow screens, every applying the acceptable motif, square measure organiz consecutive as in roller printing, however they’re align over a moving horizontal blanket that carries the material between the 2. because the material moves forward the screens rotate and apply the colour.
The swivel squeegee consists of color tube , Types of dyes and their propertiescolor basin and insertion blade.
It moves up once the printing unit is raised and it hydraulicly touched down into operating position once printing position is down.
This machine obtainable in numerous commonplace breadth of 72″,94″,100″ long for twelve,16,20 colour.
The squeegee blade is versatile to accommodate any variations in pressure needed to force the paste equally through the mesh of the screen across the breadth of the fabricfabric.
In some models, a metal rod held in place by a magnetic field replaces the squeegee. This system suits heavier fabrics better, as it limits the minimum amount of paste that can be delivered more effectively.
Rotary-screen machines generally require less pressure between the roller and fabric compared to engraved roller systems.
As with all screen printing methods, you can control paste delivery by adjusting the mesh size. Use a coarser mesh for fabrics made from thicker fibers or for solid color areas, and choose a finer mesh to produce detailed designs or to print on fabrics with fine fibers.
The advantages of rotary-screen printing machines over engraved-roller machines embody quicker production rates, larger simple putting in place and a lower dependence on expertise for in operation. laptop motor-assisted style techniques for printing screens square measure currently progressively wide used.
options of machine
1.Interchangeable rubber squeegee
2.Variable positioning of squeegee angle
3.Very correct paste level management.
ZIMMER SCREEN PRINTING
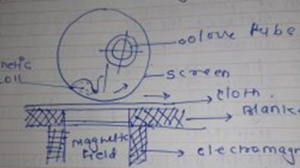
Zimmer screen printing machine speed varies from 5-150 m/min
Inside the screen are the color tube and the magnetic roll, which is held in position by a magnetic field. As the screen rotates, the magnetic roll rotates along with it, helping to transfer the print paste onto the fabric. The fabric remains attached to the moving blanket during the process.
A pump and level gauge supply the paste automatically through a tube inside the screen. The printing assembly can be adjust to fit any screen width and allows for design repeats ranging from 57 to 100 cm.
The repeats square measure set by hand wheel.
Advantages of magnetic squeeze system
1.Magnetic roller square measure amendment no end the machine
2.Automatic the paste determined.
3.The squeegee doesn’t needed sharpening.
4.Regular quantity of print paste transfer.
5.Uniform pressure exerted across the complete breadth of material.
6.Less friction between magnet roll and screen will last longer.
7.Design repeat up to a hundred and forty in. will achieved.



