Basic Designs and Its Properties
Basic Weave Structures – Plain, Satin, Twill weave and Its Properties
Basic Weave Structures:
The way the harness raises teams of warp yarns to allow the insertion of the filling yarn determines the weave pattern and, ultimately, the type of cloth produced.”Weave patterns will produce variable degrees of sturdiness in materials, adding to their quality and conjointly to their look.
There are 3 basic weaves. they’re taffeta weave, twill and weave. All alternative weaves are a variation or a mix of those weaves. textile and Rib weave are 2 variations of taffeta weave. within the same manner twill can even have variety of variations, e.g., warp featured twill, woof featured twill, even twill, uneven twill, pointed twill, herring bone twill, gabardine, corkscrew so on.
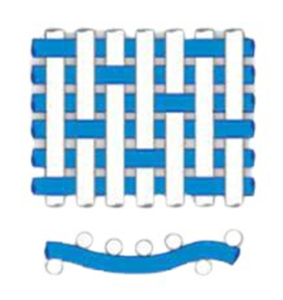
Textile designers use graph paper (also called pointed paper) to illustrate weaves or the sequence in which yarns interlace in a fabric, such as the taffeta weave. Each vertical row of squares represents a warp yarn, while each horizontal row represents a filling yarn.
When the warp yarn passes over the filling yarn, designers mark the square as a ‘raiser.’ If the warp passes under the filling, they leave the square blank, referring to it as a ‘sinker.’
Designers use graph paper to illustrate weave patterns or analyze fabric structures. However, the diagram doesn’t show the number of yarns per inch or specify yarn size or type. The final design displayed the weave structure from the fabric’s face side, which is commonly use for analysis.
Plain weave: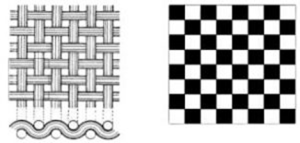
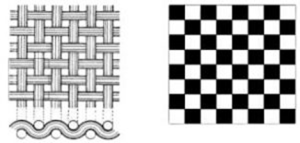
A plain weave could be a weave wherever every filling passes alternately over and beneath every warp during a sq. pattern. The complex is opposite in neighboring cells. The repeat is over 2 ends and 2 picks.
Properties of Plain weave:
Plain Weave
- Both aspects ar reversible till material is paint or written from right side.
- Fabrics have high abrasion resistance.
- No yarn slippage.
- There is no distinct style unless yarns have contrastive colours or thickness.
- Easily produced; most yardage; cheap. Medium to boring luster.
- Adaptable for printing and alternative finishing method.
- More sturdy. No floats. Medium drapability to excellent drapability.
- In previous notation technique, denoted by ‘P’. Examples: cloth, Cheese textile, Cretonne, Percale, voile.Satin weave:




A weave could be a weave wherever four (or more) shaft with warp floats in interrupted diagonal. complex are ne’er adjacent to 1 another. fabric repeat over altest five ends and five picks however the warp ends interlace just once per repeat. - Properties of fabric weave:
- Right and wrong sides look quite completely different.
- Very low abrasion resistance.
- It has interrupted diagonal discernible with simple microscope.
- It is dearer.
- glorious lusture.
- Less sturdy.
- Excellent Drapability.
- Examples: fabric, Slipper fabric, Creepe back fabric.
Twill weave: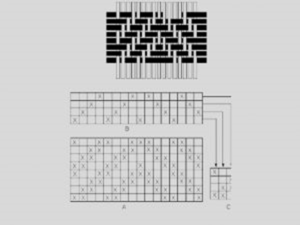
A weave characterized by diagonal lines on the face of the material. The woof or warp yarns interlace with quite one warp yarn however ne’er quite four warp yarns. On every sequent line woof moves the planning one step to the proper or the left forming the diagonal. regardless of the direction of the diagonal on the face of the material the direction is opposite on reverse.
The diagonal will vary from a coffee fourteen o angle referred to as reclining twill to a seventy five o angle referred to as a step twill. the foremost common is forty five o and is regular or medium twill twill, steeper the twill stronger the material is probably going to be. A a pair of x one twill are one wherever warp can reassess a pair of warp and beneath one woof. Suppose you’ve got 4/2 weave, then it means you may have four +2 =6 harnesses, (i.e) the repeat can have half dozen boxes horizontally and half dozen boxes vertically.
Properties of Twill weave:
- Twill weave is one in all the strongest weave.
- It has fairly smart drape.
- More tightly plain-woven.
- A twill doesn’t get dirt simply however once it gets dirt it becomes very troublesome to scrub them.
- It has smart wrinkle resistance.
- Finer yarns with high twist are utiliz in construction of twill weaves.
- Denim is Associate in Nursing uneven warp featured twill materials.
- Wefts are in white and warps are in blue therefore denim is blue on one aspect and white from the opposite aspect.
- Other variations of twill include: Pointed twill, Herring bone, Gabardine, Corkscrew twill so on.
Derivatives of Plain Weave
Features of Warp Rib
- It produces rib or cord effect in weft direction.
- Extending plain weave vertically.
- Finer yarn used as warp and coarser as weft yarn.
- The number of ends/inch are more than the number of picks/inch.
- Low twisted yarn is use as weft.
- Warp yarns are use as a single yarn and weft yarns are use as group or bundle yarns.
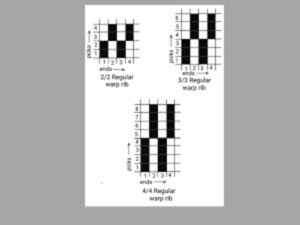
Regular warp rib:
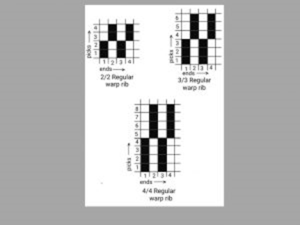
Formula number: X/X [ X=Number of warp up in repeat]
Regular appearance is show in the fabric.
Used as grosgrain cloth, mattress cloth etc.
Irregular warp rib:

Formula number: X/ Y [ X=Number of warp up in repeat and Y=Number of weft up in repeat ]
Irregular appearance is show in the fabric.
Used as grosgrain cloth, mattress cloth etc.
Features of weft rib
- It produces rib or cord effect in warp direction.
- Extending plain weave horizontally.
- Finer yarn used as weft and coarser as warp yarn.
- The number of picks/inch are more than the number of ends/inch.
- Low twisted yarn is use as warp.
- Weft yarns are use as a single yarn and warp yarns are use as group or bundle yarns.
- Used as hair cords, blankets etc.
Regular weft rib:

Formula number: 1/1 (X) [ X=Number of warp up in repeat]
Regular appearance is show in the fabric.
Irregular weft rib:
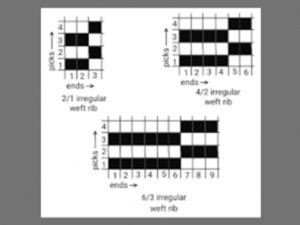
Formula number: 1/1 (X+Y)
Irregular appearance is show in the fabric.
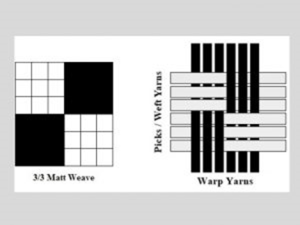
Features of Matt /Hopsack/ Basket Weaves
- It is construct by extending the plain weave both vertically and horizontally.
- Combination of warp and weft rib.
- Loose structure.
- The smallest matt weave is 2 / 2 (2) (X) matt.
- Basket weave fabrics are more flexible and wrinkle resistant because there are fewer interlacing per square inch.
- It has a greater resistance to tearing.
- Matt weaves tend to give smooth-surfaced fabrics.
Regular matt:
Formula number: X/X (X) [ X=Number of warp up in repeat]
It is produce by the combination of regular warp and weft rib weave.
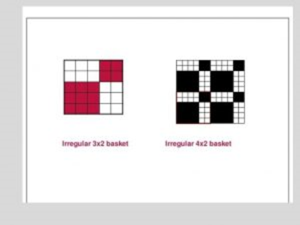
Irregular matt:
Formula number: X/Y (X+Y) [ X=Number of warp up in repeat and Y=Number of weft up in repeat]
It is produce by the combination of regular warp and weft rib weave.
Stitched matt:
Formula number: X/X (X) [ X=Number of warp up in repeat]
In this weave stitch is use to avoid looseness of yarn in the fabric.
To produce a firm cloth with lower setting, the center ends in each square can be stitch.
In warp face, the central warp yarn goes down and in weft face, the central warp yarn comes up.
Fancy matt:
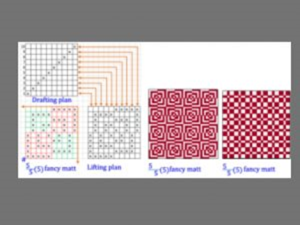
Formula number: X/X (X) [ X=Number of warp up in repeat]
In stitch matt, the stitching thread is hide by the neighbouring threads. But in the fancy matt the stitching threads are not hide, they are visible.
They produce decorative appearance on the fabric surface.
Use of matt
Matt weave finds extensive uses for a great variety of fabrics such as dress materials, shirtings, sail cloth, duck cloth etc
Classifications of Twill Weave
Twill weave can be classified in following categories
- Ordinary Twill
- Pointed/Zigzag Twill
- Broken Twill
- Combine Twill
- Herringbone Twill
- These Twill weaves are further sub classified into following categories
- Warp Face Twill
- Weft face Twill
- Balanced Twill
Warp faced Twill :
In this type of weave the warp yarn floats over all the weft yarn in a repeat except one pick e.g. 2/1, 3/1, 4/1
Weft faced Twill :
In this type of weave the weft yarn floats over all the warp yarn in a repeat except one end e.g.1/2,1/3,1/4
Balanced Twill :
In this type of twill weave the warp and weft floats are equal. These twill weaves are also called as reversible twill weaves e.g. 2/2 ,3/3,4/4
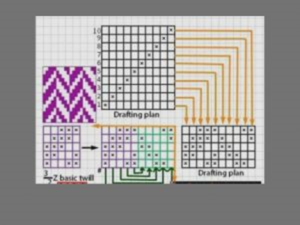
Right Hand Twill Weave :
In this the diagonal lines runs from lower left to upper right of the fabric.It is also know as Z-twill. The right hand twill gives smoother surface as compare to other twill weaves.
Left Hand Twill Weave :
In this the diagonal lines runs from top left to lower right of the fabric.It is also know as S-twill.
Pointed Twill/Zigzag Twill Weave :
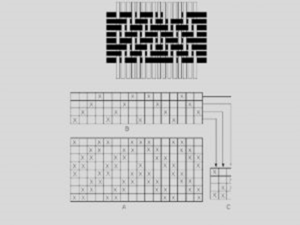
In this type of twill weave the twill line progresses in one direction for half of the repeat. Then it is reverse for the next half of the repeat.
It is the simplest and one of the most important modifications of twill weave produced by reversing the direction of twill at suitable interval.
A certain point select in this weave from which the twill line reverse and so it is sometime called as pointed twill. In this weave pointed or straight draft used.
This twill is produce by combining S and Z twist. According to reversing of direction there are two type of zigzag twill.
Horizontal zigzag twill.
This Twill produce when the basic twill extended in warp direction. In a horizontal zigzag twill the number of warp yarn in a repeat is double of the number of weft. In horizontal zigzag twill pointed draft used.
Vertical zigzag twill :
This Twill produce when the basic twill extends in weft direction. In a horizontal zigzag the number of weft yarn in a repeat is double of the number of warp. In Vertical zigzag twill straight draft used.
Herringbone Twill :
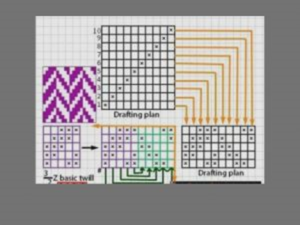
These twill weaves are same as pointed twill however the point effect is broken. This not only prevent the formation of a long float but also creates a distinct stripe effect.
Due to this reason these weaves are consider to be more advantageous than pointed twill weaves.
Transposed twill :
In this type of weave the twill line is brake by altering the original order of the yarns. This produces very creative designs. This alteration done in many ways to produce transpose weave. One of the method shown in fig.
Combined twill :
These weaves produced by the combination of two different types of twill weaves alternately. This combination can be warp wise or weft wise.
Due to this the angle of twill line effects. As in warp wise combination the twill angle is less than 45°. When the twill combines weft wise the twill angle is more than 45°.
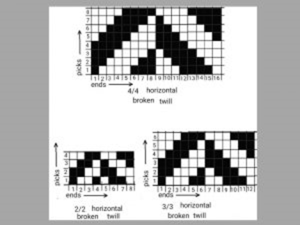
Broken twill :
These weaves produces by breaking the continuity of any continuous twill weave which can be in either regular or irregular way.
It will result in a stripe like effect so this stripe effect can be in either warp or weft direction. By using this method a large variety of designs produced. One of the method of constructing a broken twill shown in fig.
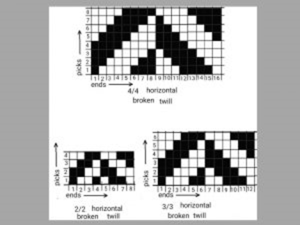
RELATED LINKS MCQ