Detail study of Loom Timing Diagram
Loom Timing
Loom timing arrangement is outlined as relative written record sequences of assorted primary and secondary motions are expressed in terms of degree of crank shaft rotation. The loom temporal arrangement is conferred by a diagram termed as “Loom temporal arrangement Diagram”. The diagram depicts the beginning and finish of every primary event of various weaving motions. the beginning and finish of events are influenced by loom type, material breadth and fabric kind. The loom temporal arrangement cycle is shown in below Figure.
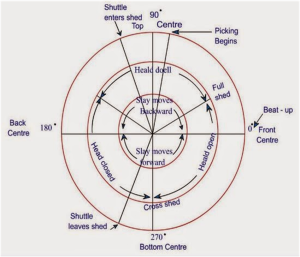
Fig: Loom temporal arrangement diagram
The timings of most of the events within the loom cycle are ruled by the position of the reed and therefore the sley. as an example, the reed should air its approach towards the rear of the loom before the shed is giant enough to admit the shuttle. This determines the temporal arrangement of the selecting mechanism that is directly associated with the position of the reed and sley.
Some others are associated with it indirectly. as an example. the temporal arrangement of the yarn break stop motion is expounded to the flight of the yarn carrier, that is ruled by the position of the reed. The timings on the weaving machine are expressed in relevancy the spatial relation of the shaft (main shaft) that operates the sley.
The path derived out by the axis of the crank pin is named the ‘crank circle’. The arrow on the crank circle shows the standard direction of rotation of the shaft. once the crank and crank arm are in line, and also the sley is in its most forward position.
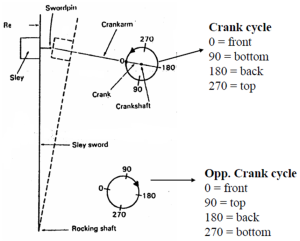
The crank circle is graduated in degrees from this time within the direction of rotation of the shaft. Any temporal arrangement may be expressed in degrees, as, as an example, ‘heald level at 3000’
Looms are supplied with a graduated disc on the shaft and a hard and fast pointer to form settings in relevancy the spatial relation of the shaft. With the reed in its most forward position, the disc is adjusted so the pointer is opposite to 00 on the graduated scale. The loom could then be turned to any desired position manually, the disc turning with it and also the pointer remaining vertical and indicating the spatial relation of the crank shaft. In fashionable looms with microprocessors, the most shaft position is displayed on a screen, however the setting principle remains same.
RELATED LINK
for more details visit our
website link
Facebook Page link
Instagram page link
Gmail-link



