QUALITY ASSURANCE & QUALITY CONTROL
Quality wordbook Definition: Quality assurance/quality management (QA/QC)
Quality assurance (QA) and internal control (QC) square measure 2 terms that square measure usually used interchangeably. though similar, there square measure distinct variations between the 2 ideas. This page can justify the variations between internal control and quality management, and supply definitions and samples of every.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN QA AND QC
Quality assurance and internal control square measure 2 aspects of quality management. whereas some quality assurance and internal control activities square measure reticulated, the 2 square measure outlined otherwise. Typically, QA activities and responsibilities cowl just about all of the standard system in one fashion or another, whereas QC may be a set of the QA activities. Also, parts within the quality system won’t be specifically line by QA/QC activities and responsibilities however could involve QA and QC. Figure one shows ISO 9000 definitions from ISO 9000:2015: Quality management systems – Fundamentals and Vocabulary.
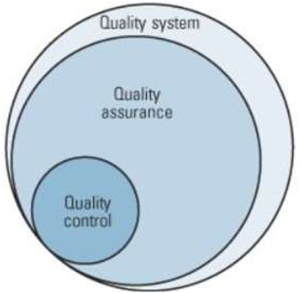
Figure 1: Quality System, Quality Assurance, and internal control Relationships Quality Assurance
It often outline as “part of quality management focuse on providing confidence that quality requirements will be consummate.” the arrogance provide by quality assurance is two fold—internally to management and outwardly to customers, government agencies, regulators, certifiers, and third parties. associate alternate definition is “all the plan and systematic activities enforce at intervals the standard system {that can|which can|that may} be incontestable to produce confidence that a product or service will fulfill needs for quality.”
Quality management
Quality control are often outline as “part of quality management focuse on fulfilling quality needs.” whereas quality assurance relates to however a method is performe or however a product is create, internal control is a lot of the review side of quality management. associate alternat definition is “the operational techniques and activities wont to fulfill needs for quality.“
INDUSTRY views ON QA AND QC
For some service organizations, the conception of {quality management|internal control} could also be foreign as a result of there’s no tangible product to examine and control. the standard assurance perform during a service organization might not embrace internal control of the service however could embrace internal control of any merchandise concerned in providing the service.
A service could embrace merchandise that square measure documents (such as a report, contract, or design) or tangible merchandise (such as a rental automotive or units of blood). it should be necessary to manage product quality during a service organization to confirm that the service meets client needs.
QA, QC, and Review
Inspection is the method of measurement, examining, and testing to measure one or a lot of characteristics of a product or service and therefore the comparison of those with fixed needs to see conformity. Products, processes, and varied different results are often inspecte to create positive that the thing coming back off a mechanical system, or the service being provide, is correct and meets specifications.
Quality Assurance and Audit Functions
Auditing is a part of the standard assurance perform. it’s vital to confirm quality as a result of it’s wont to compare actual conditions with needs and to report those results to management.
In The Quality Audit: A Management analysis Tool , Charles Mill wrote that auditing associate review don’t seem to be interchangeable: “The auditor could use review techniques as an analysis tool, however the audit shouldn’t be concern in effecting any verification activities resulting in the particular acceptance or rejection of a product or service. associate audit ought to be committe the analysis of the method and controls covering the assembly and verification activities.”
Formal management systems have evolved to direct and management organizations. There are quality management systems (QMSs) as well as environmental or different management systems, and every of those systems could also be audit.
HISTORY OF QA AND QC
Quality has been outline as fitness to be use, agreement to needs, and therefore the pursuit of excellence. albeit the conception of quality has existe from early times, the study and definition of quality are given prominence solely within the last century.
1920s: internal control
Following the economic Revolution and therefore the rise of production, it became vital to raised outline and management the standard of merchandise. Originally, the goal of quality was to confirm that engineering needs were met in final merchandise. Later, as producing processes became a lot of advanced, quality developed into a discipline for dominant method variation as a method of manufacturing quality merchandise.
1950s: Quality Assurance and Auditing
The quality profession enlarged to incorporate the standard assurance and quality audit functions. The drivers of freelance verification of quality were primarily industries during which public health and safety were preponderating.
Scope of Quality Assurance
Yarn spinning may be a method of creating or changing fiber materials into yarns. it’s a posh branch of textile. Here the task of internal control starts from the staple. initially once the raw cotton arrives, the workplace boys collect samples from every bale and provides several numbers to every bale. Then the samples ar tested in H.V.I. machine. From the obtained results, the bales ar categorised in appropriate classes for bale management and hold on within the warehouse. Then the raw cotton is fed to the blow area through the bale management system. The bale management system may be a important task of the standard Assurance department in spinning mill.
In blowroom, the fibers ar opened and cleansed by beaters. Here if over beating takes place then there’s an opportunity of fiber injury. So, the standard assurance department tests cotton sample before and once each beating position to see the improvement potency and fiber damaging. From there, necessary actions ar taken. totally different wastes that ar collected at the fiber deposition plant of blow area also are studied to assure correct removal of trash particles likewise as least doable wastage of cotton fiber. conjointly the standard assurance department in spinning mill monitors the setting and performance of the contamination extractor of the blow area.
In the carding machine the Ktex of the created sliver is checked once per shift. The performance of the carding is evaluate by testing m/c and sliver of the carding in USTER-5 and AFIS. From there the Neps Removal potency, SFCw, SFCn, UQL etc ar seen to guage its performance and necessity of gauge amendment, grinding and wire amendment of cylinder, licker-in and flat is decide. the cardboard sliver is tested in USTER-5 once per shift to check its Unevenness (U%) and constant of variation of mass (CV%).
In breaker draw frame, in the main the grain/yd of sliver is test once per shift. apart from this conjointly the sliver is test in USTER-5 to work out the length of the fibers in strand to line the right roller gauge within the roller drafting zone. The breaker sliver is test once per shift in USTER-5 to work out its Unevenness (U%) and constant of variation of mass (CV%).
In lap former, the lap thickness is measure in the main.
The Comber is a awfully crucial machine. Its performance plays an important role on the standard of the combed yarn. So, the performance of the comber is assessed by testing the fabric before and once it. From there the nep removal potency of the machine is decide. conjointly the noil is test to envision whether or not long fibers ar being wasted throughout the process. From there, the required changes within the setting of the machine is dole out. The grain/yd of combed sliver is checked once per shift. The combed sliver is additionally tested once per shift in USTER-5 to work out us, CVA etc and any periodic faults from the photo.
The finisher draw frame may be a terribly important machine in respect of internal control. because it is that the last machine fitted with Associate in Nursing automobile radical, it’s the last step wherever the mass variation of sliver will be maintained. For this here the grain/yd of sliver is checked at each hour. If the variation of the finisher sliver will be controlled, then there’ll be less variation and imperfectness within the yarn. conjointly the standardization of the auto-leveler is completed once necessary by the QA department. The finisher sliver is tested once per shift in USTER-5 to work out its us, CVm%, CV3m% and to envision whether or not there’s any periodic fault from the photo.
Introduction:
Poor quality in spinning is also outlined as a mix of things like the technical parameters of yarn being out of the appropriate tolerance limits of the shoppers, presence of objectionable faults and labels, improper packing resulting in damages whereas handling, shabby packing leading to time consumption whereas gap and additional house for storage, delay in despatch inflicting loss to the client and penalty to the corporate, exaggerated value of producing pushing the organization to a loss, short provides and over productions resulting in accumulation of finished material as stock. However, in follow, the nomenclature of quality is employed for product parameters by the technicians in workplace, except for the highest management, everything is very important because the company’s profit depends on the overall quality and not solely on the technical parameters. The technicians, therefore, ar advised considering everything along and not concentrating solely on the technical parameters.
- Raw material
There is a right away relationship between sure quality characteristics of the fibre and people of the yarn. Seventy to eighty % of basic yarn quality is determine by the material. The fibre properties just like the staple length, uniformity in staple length, short fibre contents, fineness, strength, elongation, maturity, etc., play a job.
</ul
- Raw material
>
If the micronaire is coarse, the quantity of fibres within the yarn cross section are going to be less. This perpetually leads to lower strength and lower elongation. however it’s simple to method coarse micronaire fibres in blow room and cards. Nepping tendency is a smaller amount for coarse micronaire fibres. On the contrary, suitableness (in each speed frame and ring frame) isn’t smart with coarser micronaire fibres. united states is plagu by micronaire.
Coarser the micronaire, higher shall be the united states. Coarser the fibre, higher the top breakage rate in spinning. Uster skinny place (30%) within the yarn vary relying upon the fibre micronaire. Lower the micronaire lower the skinny places and the other way around.
Raw materials if not appropriate for the merchandise being create cannot provide the standard parameters pro re nata. we’d like to know the standard objectives of the merchandise and judge the raw materials.
The factors like feel of the material, visual aspect within the surface of cloth, strength of the yarn and therefore the cloth and dye ability area unit ruled by the material properties.
simply by defrayment extra money on superior fine cotton cannot provide the standard needed by the client, however shall increase the value of manufacture resulting in a loss to the corporate.Raw material ought to be appropriate for the machine being worked.
The machines area unit commonly designed for a spread of raw materials, and that we would like sure modifications whereas operating. the kind of gap machines differs from cotton to synthetics, and conjointly with within the cottons itself from fine to superfine cottons. Coarser wire points area unit used for carding polyester, whereas for cottons we’ve completely different wire configuration. The nose plates area unit completely different for cotton and polyester.
In ring frames, giant diameter bottom rollers of thirty millimetre area unit used for long staple synthetic fibres compared to 27- or 25-mm diameter for cottons. The cradle sizes employed in drafting area unit completely different for various staple lengths. Similarly, there area unit range of changes within the machine configuration to suit completely different raw materials. If we tend to don’t seem to be clear regarding constant, inspite of getting latest machinery and smart raw materials, we’d manufacture unhealthy quality yarns.Variations, mix-ups, contaminations and damages in raw materials are chargeable for poor quality yarns. the choice of raw materials for the merchandise and therefore the machines play an important role in obtaining the specified quality. with the exception of the choice of raw materials, the ways that within which they’re handled and used conjointly play a crucial roleFollowing area unit some examples for poor quality in ring spinning:</st
- rong>
- Improper choice of material
- Variations in material
- Handling and storage damages
- Damages because of improper ginning in case of Cotton
- Fused fibres just in case of artificial staple fibres
- Presence of uncut fibres in staple fibres
- Packing of cotton bales with polyester cotton cloths/HDPE/polypropylene cloths
- Inadequate range of tons in a very combining
- Reasons for poor quality in mixing:
- Not substantiative the heap numbers and bale numbers before taking the blending
- Taking additional bales from tons for combining
- Not clearly defining/understanding the amount of materials to be taken from every combining part
- Uncontrolled combining of soppy wastes
- Putting all soft wastes at one place in a very stack
- Not taking materials from every bale uniformly whereas creating a stack combining
- Not keeping the bales in allotted place whereas combining or feeding to bale pluckers
- Not removing the Hessian/HDPE covering and bale hoops properly
- Not gap the cottons completely
- Not removing the massive visible contamination whereas gap the bales and doing combining
- Keeping chappals/slippers, etc., close to the blending bin
- Not cleanup the ground completely before birthing a replacement combining
- Not change the identification boards
- Pouring additional water/cotton spray oil at one place
- Handling the blending in wet condition
- Sleeping on the blending bin throughout leisure hours
- Reasons for poor quality in blowroom:
- Improper choice of cleanup and gap points for the blending in hand
- Not cutting {the combining|the blending} vertically whereas feeding to mixing bale opener
- Using improperly conditioned combining just in case of stack combining
- Feeding huge lumps of cotton to bale breaker
- Widening the settings to own additional production
- Too shut a setting leading to over beating and fibre damages
- Laps of longer lengths
- Applying excessive weights on lap spindles to induce a compact lap
- Not removing the accumulated wastes in time leading to back firing and waste contaminations
- Not cleanup the magnets on time
- Not properly closing the doors
- Not properly following color codification for laps
- Not maintaining the work space clean
- Not cleanup the sensors in image electrical controls
- Using of bent lap rods
- Using torn filter baggage
- Cleaning the machines with brooms whereas operating
- Using compressed gas for cleanup whereas machines area unit operating
- Reasons for poor quality in carding:
- Bringing the laps on head or by touching it to the body
- Not properly feeding the laps leading to doubles or singles in sliver
- Not removing the doubles and singles
- Not removing the wastes in time
- Not keeping the carding space clean
- Not cleansing the cardboard sides with a clean broom stick frequently
- Twisting an excessive amount of whereas piecing the slivers
- Not following the right color codification and channeling
- Not removal the cards in time
- Not removing the accumulated flat strips in time
- Not cleansing the Phillipson rollers in time
- Making the stop motions inactive
- Keeping the doffer cover whereas running
- Keeping the facet covers and belt guards open
- Over filling the cans
- Not removing the wastes from will bottom before inserting below coiler
- Using broken cans and spring plates
- Not cleansing the castors frequently
- Pressing the sliver within the will by hand
- Not covering the sliver in cans that area unit available
- Use of compressed gas for cleansing whereas machine is functioning
- Reasons for poor quality in draw frames:
- Not creeling the cans as per the allocation given (Card range wise or drawing delivery wise)
- Keeping the feeding cans abundant removed from the basket
- Overlapping the slivers whereas piecing within the basket
- Cutting the sliver in cans at basket and reversing for adjusting the cans in basket
- Not removing the sliver wastes from the spring bottom before swing cans within the machine
- Not removing the slivers from the will whenever there’s a covering
- Making the stop motions inactive
- Not obtaining the cots buffed in time
- Replacing the highest rollers while not validating the diameter and surface condition
- Not greasing the highest roller bushes in time with correct grease
- Using sharp knives to get rid of covering leading to broken cots
- Not removing the suction box wastes in-time
- Keeping the suction box doors [*fr1] open
- Putting cotton pads to induce pressure on drafting rollersUsing broken cans and is derivedUsing nails and
- hammer to get rid of cotton from crowded trumpets
- Using trumpets while not validating their size and condition
- Not making certain correct alignment of will
- Not following the right color codification and channeling
- Over filling the cans
- Pressing the sliver in will by hand
- Use of compressed for cleansing whereas machine is functioning
- Un-staggered sliver piecing
- Checking the wrapping sporadically and correcting the helix by ever-changing the pinion
- Reasons for poor quality in combers:
- Bigger laps
- Applying excessive pressure to require compact laps
- Use of worn-out blank spools in lap forming machine
- Allowing overlapping of slivers being fed to lap former
- Overlapping the lap sheet whereas piecing
- Overlapping the slivers on table for piecing
- Not cleansing the highest combs in-time
- Not removing the accumulated comber noils in-time
- Keeping tools, etc., on the sliver table
- Inactivating the stop motions
- Piecing the slivers by over twisting
- Not following the right color codification and channeling
- Over filling the cans
- Using broken sliver trumpets
- Pressing the sliver within the cans by hand
- Use of compressed gas for cleansing whereas machine is functioning
- Reasons for poor quality in speed frames:
- Cutting the slivers at cans within the basket and distributing to alternative cans
- Overlapping the slivers whereas attending a sliver run out
- Cross creeling of cans
- Sliver rupture of guide roller
- Twisting too exhausting whereas piecing
- Applying cotton to the highest arms to induce pressure
- Pressing the front high cot to correct a unfinished business
- Not validating the spacers and condensers whereas replacement
- Not swing back the fallen floating condenser whereas attending an occasion
- Not following the right color codification and channeling
- Not removing the accumulated clearer wastes on time
- Reasons for poor quality in ring frames:
- Keeping roving bobbins on the highest of basket for very long time
- Overlapping of roves whereas replacement
- Putting cotton in high arms for obtaining additional pressure
- Using sharp knives/hooks for removing covering
- In active bottom clearers leading to partial covering
- Not attending an occasion for an extended time
- Cross-creeling
- Not removing the last layers within the roving winder and permitting it run out absolutely
- Keeping roving bobbins within the path of roving or on the highest arms
- Keeping the bobbins within the path of air flow of overhead cleaners
- Not removing the bobbins whereas a tape is cut
- Not following the running-in schedule of rings properly
- Keeping excess travellers in the cup and not removing them whereas ever-changing counts
- Not cleansing the rings with dry cloth/cotton before replacement a burnt human
- Piecing from over the cot
- Double piecing at cop bottom
RELATED LINK



